- Pathwise estimation of covariate balancing propensity scores.
- Extract coefficients from a balnet object.
- Extract coefficients from a cv.balnet object.
- Cross-validation for balnet.
- Plot diagnostics for a
balnetobject. - Plot diagnostics for a
cv.balnetobject. - Predict using a balnet object.
- Predict using a cv.balnet object.
- Print a balnet object.
- Print a cv.balnet object.
-- B --
balnet()
-- C --
coef.balnet()
coef.cv.balnet()
cv.balnet()
-- P --
plot.balnet()
plot.cv.balnet()
predict.balnet()
predict.cv.balnet()
print.balnet()
print.cv.balnet()
Pathwise estimation of covariate balancing propensity scores.
Description
Fits regularized logistic regression models using covariate balancing loss functions, targeting the ATE, ATT, or treated/control means.
Usage
balnet(
X,
W,
target = c("ATE", "ATT", "treated", "control"),
sample.weights = NULL,
nlambda = 100L,
lambda.min.ratio = 0.01,
lambda = NULL,
penalty.factor = NULL,
groups = NULL,
alpha = 1,
standardize = TRUE,
thresh = 1e-07,
maxit = as.integer(1e+05),
verbose = FALSE,
num.threads = 1L,
...
)Arguments
X |
A numeric matrix or data frame with pre-treatment covariates. |
W |
Treatment vector (0: control, 1: treated). |
target |
The target estimand. Default is ATE. |
sample.weights |
Optional sample weights. If |
nlambda |
Number of values for |
lambda.min.ratio |
Ratio between smallest and largest value of lambda. Default is 1e-2. |
lambda |
Optional |
penalty.factor |
Penalty factor per feature. Default is 1 (i.e, each feature recieves the same penalty). |
groups |
An optional list of group indices for group penalization. |
alpha |
Elastic net mixing parameter. Default is 1 (lasso). 0 is ridge. |
standardize |
Whether to standardize the input matrix. This should only be set to |
thresh |
Coordinate descent convergence tolerance, default 1e-7. |
maxit |
Maximum total number of coordinate descent iterations, default is 1e5. |
verbose |
Whether to display information during fitting. Default is |
num.threads |
Number of threads, default is 1. |
... |
Additional internal arguments passed to solver. |
Value
A fit balnet object.
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
fit <- balnet(X, W)
# Print path summary.
print(fit)
#> Call: balnet(X = X, W = W)
#>
#> Control (path: 51/100)
#> Nonzero Mean |SMD| Lambda
#> 1 0 0.05624 0.34194
#> 2 1 0.05580 0.32640
#> 3 1 0.05542 0.31157
#> ...
#> 49 16 0.02941 0.03667
#> 50 17 0.02828 0.03500
#> 51 18 0.02796 0.03341
#>
#> Treated (path: 31/100)
#> Nonzero Mean |SMD| Lambda
#> 1 0 0.13123 0.79787
#> 2 1 0.12886 0.76161
#> 3 1 0.12915 0.72699
#> ...
#> 29 9 0.14532 0.21691
#> 30 9 0.14071 0.20705
#> 31 10 0.13410 0.19764
# Plot path diagnostics.
plot(fit)
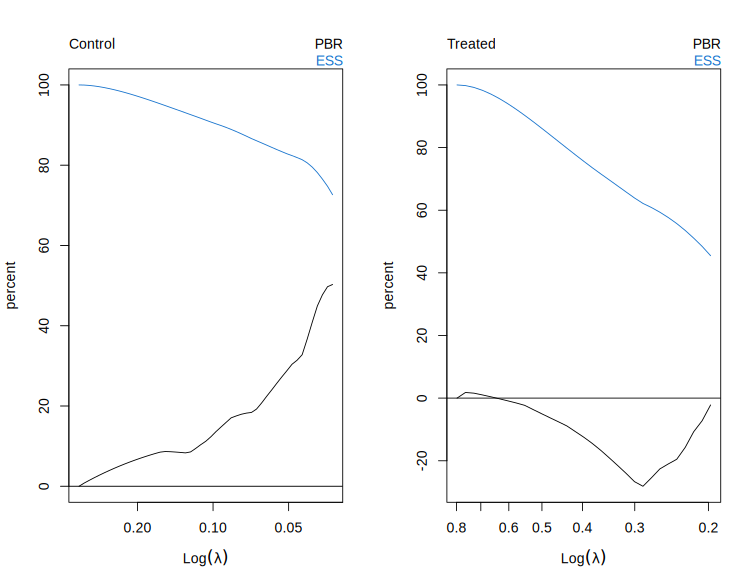
# Plot covariate imbalance at the end of the path (closest to lambda = 0).
plot(fit, lambda = 0)
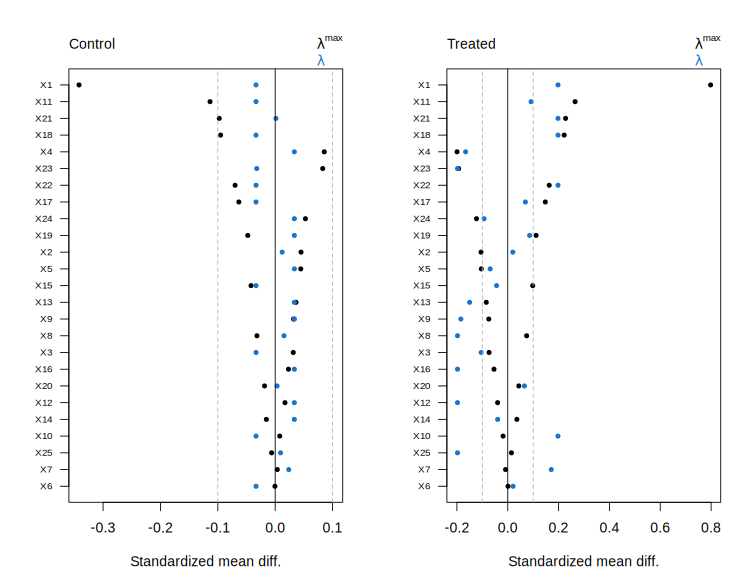
# Predict propensity scores.
pp <- predict(fit, X)
# Extract coefficients.
coefs <- coef(fit)
Extract coefficients from a balnet object.
Description
Extract coefficients from a balnet object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'balnet'
coef(object, lambda = NULL, ...)Arguments
object |
A |
lambda |
Value(s) of the penalty parameter
|
... |
Additional arguments (currently ignored). |
Value
The estimated coefficients.
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
fit <- balnet(X, W)
# Extract coefficients.
coefs <- coef(fit)
Extract coefficients from a cv.balnet object.
Description
Extract coefficients from a cv.balnet object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'cv.balnet'
coef(object, lambda = "lambda.min", ...)Arguments
object |
A |
lambda |
The lambda to use. Defaults to the cross-validated lambda. |
... |
Additional arguments (currently ignored). |
Value
The estimated coefficients.
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
cv.fit <- cv.balnet(X, W)
# Extract coefficients at cross-validated lambda.
coefs <- coef(cv.fit)
Cross-validation for balnet.
Description
Cross-validation for balnet.
Usage
cv.balnet(
X,
W,
type.measure = c("balance.loss"),
nfolds = 10,
foldid = NULL,
...
)Arguments
X |
A numeric matrix or data frame with pre-treatment covariates. |
W |
Treatment vector (0: control, 1: treated). |
type.measure |
The loss to minimize for cross-validation. Default is balance loss. |
nfolds |
The number of folds used for cross-validation, default is 10. |
foldid |
An optional |
... |
Arguments for |
Value
A fit cv.balnet object.
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
cv.fit <- cv.balnet(X, W)
# Print CV summary.
print(cv.fit)
#> Call: cv.balnet(X = X, W = W)
#>
#> Lambda min (balance loss):
#> Arm Nonzero Mean |SMD| Lambda Index
#> Control 16 0.03727 0.04918 36
#> Treated 10 0.05971 0.08806 34
# Plot at cross-validated lambda.
plot(cv.fit)
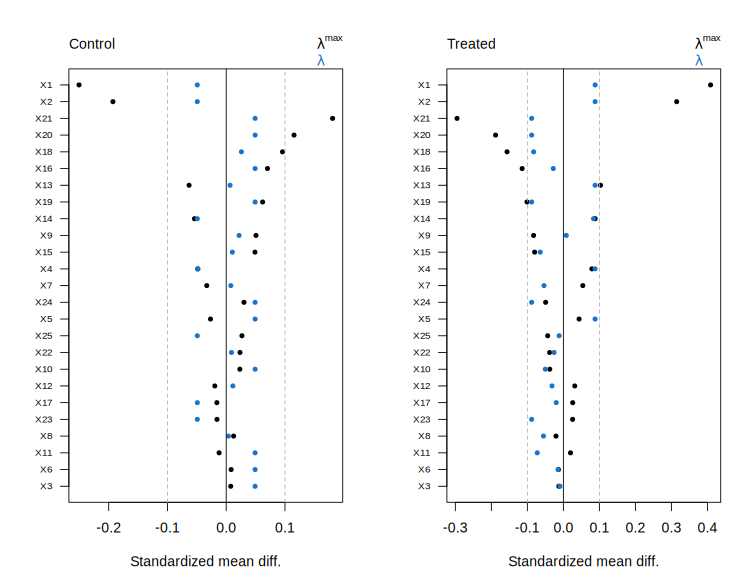
# Predict at cross-validated lambda.
pp <- predict(cv.fit, X)
# Extract coefficients at cross-validated lambda.
coefs <- coef(cv.fit)
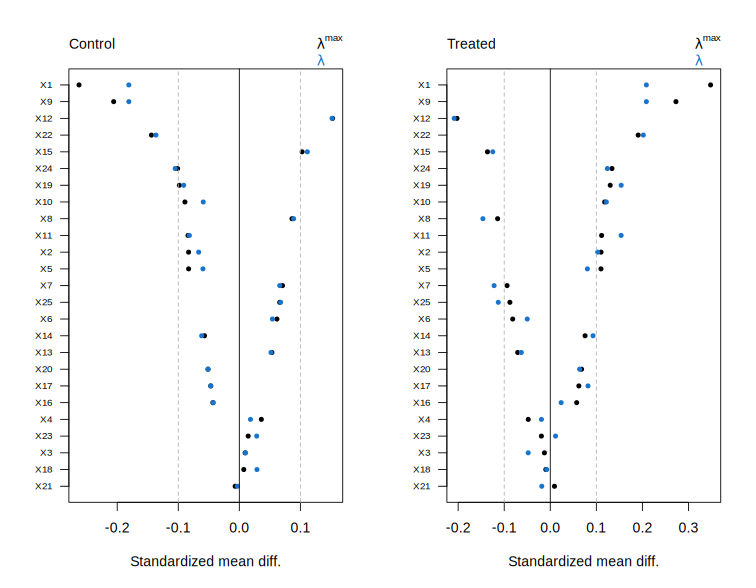
Plot diagnostics for a balnet object.
Description
Plot diagnostics for a balnet object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'balnet'
plot(x, lambda = NULL, groups = NULL, max = NULL, ...)Arguments
x |
A |
lambda |
If NULL (default) diagnostics over the lambda path is shown. Otherwise, diagnostics for a single lambda value is shown. (if target = "ATE", lambda can be a 2-vector, arm 0 and arm 1.) |
groups |
A list of group indices. |
max |
The number of covariates to display in balance plot. Defaults to all covariates. |
... |
Additional arguments. |
Value
Invisibly returns a list with the information underlying the plot.
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
fit <- balnet(X, W)
# Plot path diagnostics.
plot(fit)
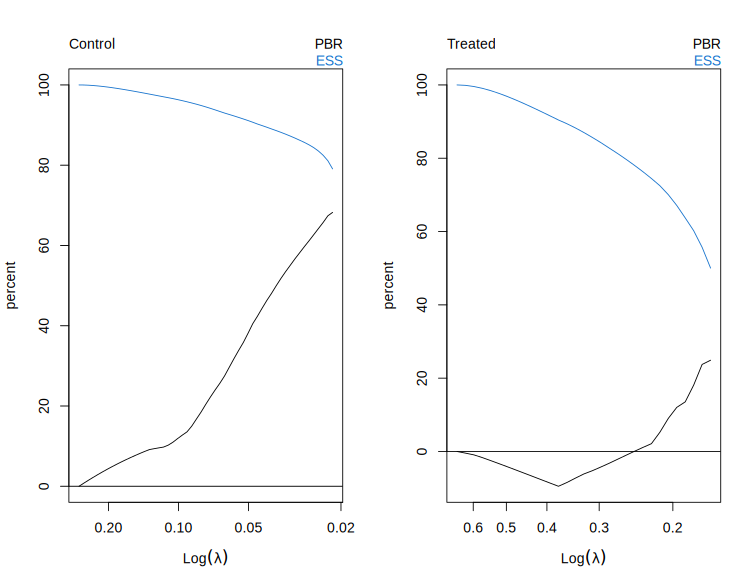
Plot diagnostics for a cv.balnet object.
Description
Plot diagnostics for a cv.balnet object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'cv.balnet'
plot(x, lambda = "lambda.min", ...)Arguments
x |
A |
lambda |
The lambda to use. Defaults to the cross-validated lambda. |
... |
Additional arguments. |
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
cv.fit <- cv.balnet(X, W)
# Plot at cross-validated lambda.
plot(cv.fit)
Predict using a balnet object.
Description
Predict using a balnet object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'balnet'
predict(object, newx, lambda = NULL, type = c("response"), ...)Arguments
object |
A |
newx |
A numeric matrix. |
lambda |
Value(s) of the penalty parameter
|
type |
The type of predictions. |
... |
Additional arguments (currently ignored). |
Value
Predictions.
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
fit <- balnet(X, W)
# Predict propensity scores.
pp <- predict(fit, X)
Predict using a cv.balnet object.
Description
Predict using a cv.balnet object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'cv.balnet'
predict(object, newx, lambda = "lambda.min", type = c("response"), ...)Arguments
object |
A |
newx |
A numeric matrix. |
lambda |
The lambda to use. Defaults to the cross-validated lambda. |
type |
The type of predictions. |
... |
Additional arguments (currently ignored). |
Value
Predictions.
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
cv.fit <- cv.balnet(X, W)
# Predict at cross-validated lambda.
pp <- predict(cv.fit, X)
Print a balnet object.
Description
Print a balnet object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'balnet'
print(x, digits = max(3L, getOption("digits") - 3L), max = 3, ...)Arguments
x |
A |
digits |
Number of digits to print. |
max |
Total number of rows to show from the beginning and end of the path |
... |
Additional print arguments. |
Value
Invisibly returns a data.frame with the printed information.
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
fit <- balnet(X, W)
# Print path summary.
print(fit)
#> Call: balnet(X = X, W = W)
#>
#> Control (path: 51/100)
#> Nonzero Mean |SMD| Lambda
#> 1 0 0.04090 0.16682
#> 2 1 0.04106 0.15924
#> 3 1 0.04121 0.15200
#> ...
#> 49 20 0.01589 0.01789
#> 50 20 0.01518 0.01707
#> 51 20 0.01483 0.01630
#>
#> Treated (path: 21/100)
#> Nonzero Mean |SMD| Lambda
#> 1 0 0.14500 0.59147
#> 2 1 0.14460 0.56458
#> 3 1 0.14488 0.53892
#> ...
#> 19 8 0.15084 0.25603
#> 20 8 0.15647 0.24439
#> 21 12 0.16712 0.23329
Print a cv.balnet object.
Description
Print a cv.balnet object.
Usage
## S3 method for class 'cv.balnet'
print(x, digits = max(3L, getOption("digits") - 3L), ...)Arguments
x |
A |
digits |
Number of digits to print. |
... |
Additional print arguments. |
Examples
n <- 100
p <- 25
X <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p)
W <- rbinom(n, 1, 1 / (1 + exp(1 - X[, 1])))
# Fit an ATE model.
cv.fit <- cv.balnet(X, W)
# Print CV summary.
print(cv.fit)
#> Call: cv.balnet(X = X, W = W)
#>
#> Lambda min (balance loss):
#> Arm Nonzero Mean |SMD| Lambda Index
#> Control 8 0.05793 0.08841 31
#> Treated 4 0.15939 0.28775 18